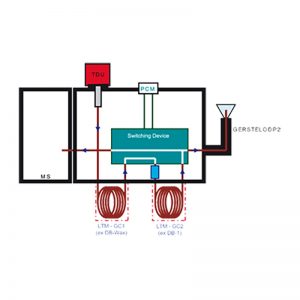
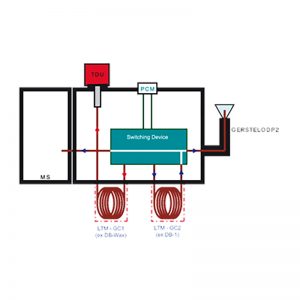
Cryogenic Trapping System (CTS)
Cryofocusing for enhanced separation performance
The GERSTEL CTS is used for cryogenic trapping and concentration of analytes. The CTS enables improved separation and lower detection limits. Following the concentration step, analytes are introduced to the GC column using a highly accurate temperature program. The CTS can be used in a single-column GC system placed at the head of the column or between the pre-column and the analytical column in a multidimensional system in order to refocus analytes prior to analytical separation.